Abstract
Ron Fredericks writes: Engineers want to build compelling products that meet their project requirements. Corporate executives want to invest in innovative people that build products that, in turn, meet their market’s window; while, both want to stay within budget. Yet both groups may feel overwhelmed with the prospect of expressing the very heart of their inspiration at some critical times during the life of these projects. In today’s post, I try to address this issue from the engineer’s perspective reaching out to the financial decision makers that ultimately control the purse strings of every project.
Table of Contents
Introducing Financial-Speak to Engineers
ROI Example: Embedded Linux
Evaluating Incremental Cash Flows
ROI Example: Simple Project Comparisons Using Net Present Value
ROI Example: Evaluating an Infrastructure Project
ROI Example: The Original Design Manufacturer
References
Errors and Changes Planned for this Blog Post
Introducing Financial-Speak to Engineers
In a previous post I introduced the idea that ethics might be the common framework between this dichotomy in communication between engineers, marketers, and executives. In this post, I suggest that engineers might apply this ethical approach by taking some time out to learn the language of business development from a financial management perspective – a conversational framework suitable for an interdisciplinary team concerned with engineering risk and strategic business value, but expressed using financial definitions.
The term Return On Investment (ROI) can be used for all three disciplines: engineering, marketing, and finance. ROI is just vague enough to cover most any discussion an engineer may encounter through-out the life of a project: from the initial decision to fund your project, to evaluating change requests during the design, build, test, and deployment cycle of an ongoing project. Evaluating ROI from a financial perspective is an ethical approach to decision-making because the financial terms I promote for this ethical framework have very precise meanings. So precise in fact, that I too have had to go back and rewrite several sections of this blog post thanks to One Nomad’s Blog comments received in this blog’s first posting.
It was the lack of financial precision embedded within my first draft for this blog post which my guest reader used to convince me of my own mistakes. Yet to be clear, identifying my mistake is also my gain. Effective communication is a process of two or more people sharing ideas…
Learning to converse and plan using financial terms for ROI decision-making can level the playing field between engineers, marketers, and business executives since ROI itself is not a common financial term. Engineers practicing Financial-Speak centered around ROI as the goal, can help reduce many of the common problems related to individuals trying their best to participate in team decision making. This leveling of the playing field – between team members – can also enhance the power of their conversation, leading the way for the much sought after innovations that are in popular demand today.
Consider building a financial model around ROI before presenting your most important technical needs to executives, marketers, and other decision makers. Read on to learn how. Of course ROI from a financial perspective is not the only way to build effective interdisciplinary teams with engineers involved. In a future post I may suggest a corollary to this ethical approach for executives and marketers who would like to reach out to engineers – using Six Sigma, CMMI, and emerging techniques developed by Dr. Thomas J. Buckholtz as useful processes seeped in ROI terminology.
Figure 1: Net Present Value Equation
![NPV(CF_k, R, IV) := IV+delim{[}{sum{k=1}{N}{CF_k/(1+R/100)^k}}{]} NPV(CF_k, R, IV) := IV+delim{[}{sum{k=1}{N}{CF_k/(1+R/100)^k}}{]}](https://www.embeddedcomponents.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_952.5_bfeb240f8e08138085d65c76df21909d.png)
Where:
 is the Net Present Value function, in dollars
is the Net Present Value function, in dollars
 is a project’s Cash Flow, in dollars
is a project’s Cash Flow, in dollars
 is the hurdle Rate, in percent per period
is the hurdle Rate, in percent per period
 is the Initial Investment (a negative number), in dollars
is the Initial Investment (a negative number), in dollars
And:
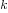 is the cash flow’s time increment, or period
is the cash flow’s time increment, or period
 is the total number of cash flow periods for
is the total number of cash flow periods for 
Time increment for  and
and  might be in years, quarters, or months, for example
might be in years, quarters, or months, for example
ROI Example: NPV’s Effect on Embedded Linux
The equation in Figure 1 forms the heart of my “ethics in engineering” proposal. Namely, the sooner a new device gets to market, the sooner a firm can realize new income. New income realized sooner, is much better than income realized later. A finance discussion around NPV would call this time’s negative impact on the value of money. I’m talking about the exponential effect that the prevailing interest rate, R, has in the NPV equation shown in figure 1.
A few years ago several of the leading embedded operating system suppliers used this equation to show that embedded Linux was a poor choice for new embedded device development projects. One such paper published by Dr. Jerry Krasner in 2003, Total Cost of Development, presents the typical argument pretty well. At that time Dr. Krasner and many others may have been right. Now in 2007, times have changed significantly. A recent blog entry on CNET shows the missing element from Dr. Krasner’s report and is a Harold for the embedded industry going forward: Oracle touts Linux deals.
How times have changed…
Because of the significant adoption of Linux in enterprise projects, the total project cost of using embedded Linux has gone down too. Indeed, the migration and reuse of enterprise Windows operating system application programming interfaces (API’s), kernel components, and development tools into embedded device projects was a key part of Dr. Krasner’s report, see link above. Dr. Krasner concluded at the time that embedded Windows CE made the best choice for new projects from a total cost of ownership perspective – just another way of looking at NPV!
Now the ROI benefits behind projects that select embedded Linux follows Dr. Krasner’s logic perfectly. Embedded Linux is now experiencing the same reduced total cost of ownership that only embedded Windows CE enjoyed just a few years ago. The reduced total cost of ownership comes from new and improved tools, components, and API’s that cross over from enterprise projects to the embedded marketplace. There is a significant overlap in Linux kernel updates, components, and tools driven by enterprise projects that are also suitable for use in embedded projects.
The available pool of engineers that know how to work with Linux can now support embedded development projects that use embedded Linux too. The marketing movement around the value and excitement of using Linux may also reduce the cost of taking an embedded device to market. In short: lower upfront costs, more options, more solutions, and faster time to market. Even Dr. Krasner has decided to post an update to his old white paper showing total cost of development to be favorable for embedded Linux projects. Download his updated paper.
None of these enterprise driven benefits exist with respect to the traditional embedded real-time operating system (RTOS). To be clear, there are other benefits to using an RTOS. I discuss one significant benefit to using an RTOS in another post: How to Leverage the Value of a Board Support Package.
Evaluating a Project’s Incremental Cash Flow
NPV is just one example of applying the principle of ROI to making project decisions. NPV falls into the general category of capital budgeting, a process of evaluating proposed investments into new projects. The capital budgeting process is concerned only with incremental cash flows. So the vague concept of ethics can be transformed into a specific financial discussion.
Two financial functions can measure time’s effect on money:
(1) Net Present Value (NPV) expressed as a monetary value,
and
(2) Internal Rate of Return (IRR) expressed as a percentage.
Where:
Net Present Value (NPV) of a capital budgeting project is the dollar amount of change in the value of the firm as a result of undertaking the project [Ref: Financial Management: Principles and Practice P.234]. The mathmatic definition for NPV is:
NPV = IV + Sum[ CF(k) / (1+R)^k ], k ranges from 1 to N
Where:
IV = Initial Investment (a negative number)
CF(k) = cash flow value (project outputs – project inputs) for period k
R = hurdle rate per period
period = a unit of time, typically year, quarter, or month
N = total number of periods for the project
Present Value (PV) is the value today of a future, or expected, cash flow. The mathematic definition for PV is:
PV = Sum[ CF(k) / (1+R)^k ], k ranges from 1 to N
NPV can be expressed in termis of its present value (PV):
NPV = IV + PV
Hurdle Rate is the required rate of return before launching a new project. The hurdle rate must be carefully chosen. It can be expressed as a percent per period. The period is commonly defined as one year, but other convenient time period could be selected such as one quarter, or one month. The same unit of time will need to be associated with cash flow. Other rate terms can be used in addition to, or instead of, hurdle rate: discount rate, cost of capital, or interest rate.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR) is the discount rate at which the
NPV of the project is zero. [Ref: Financial Management: Principles and Practice P.240]. The mathematic definition for IRR is related to NPV:
0 = IV + Sum[ CF(k) / (1+IRR)^k ], k ranges from 1 to N
NPV and IRR are related to each other:
What follows is a list of relationships between NPV and IRR. Use these relationships after calculating the NPV and IRR for each of the proposed project alternatives.
(1) If NPV(CF,R, IV) = 0,
then the hurdle rate, R = IRR
(2) For any set of cash flows estimated for a prospective project,
there is only one value for NPV.
But, the same project model can result in several IRR values,
where NPV = 0.
(3) If IRR > Hurdle Rate,
then a prospective project may make an acceptable
investment.
(4) If IRR >> Hurdle Rate (i.e. significantly greater than),
then a prospective project may carry too much risk.
(5) The hurdle rate includes both a minimum desired rate
of return for a project, and a threshold representing risk.
(5-a) A typical hurdle rate for an E-Business project
might be 15%.
(5-b) A typical hurdle rate for an embedded systems project
might be 18%.
(5-c) Embedded Components, Inc. is focused on lowering risk
for its members by promoting the re-use of pre-existing
components through its online marketplace
for embedded device manufacturers and their
communities.
(6) In general seek to maximize NPV, not IRR.
(7) Yet, if two projects have NPV curves that cross over each
other,
then the interest R where the curves cross is called
the Crossover Point.
(7-a) If the Crossover Point > IRR,
then accept the project with higher NPV.
(7-b) If the Crossover Point < IRR,
then accept the project with higher IRR.
(8) An NPV value of zero also means the investment into that
project would neither gain nor loose value for the company.
Read the rest of this entry »
Technorati Tags: Ron Fredericks, Engineer, project, requirements, executive, invest, budget, financial management, Return On Investment, Six Sigma, CMMI, Dr. Thomas J. Buckholtz, cash flow, Net Present Value, Internal Rate of Return, Hurdle Rate

 td (propagation time delay assigned to each gate)
td (propagation time delay assigned to each gate) td (propagation time delay assigned to the D FlipFlop)
td (propagation time delay assigned to the D FlipFlop) tripdt (td’s accuracy band assigned to each gate including the D FlipFlop)
tripdt (td’s accuracy band assigned to each gate including the D FlipFlop) logical high value for each gate and D FlipFlop
logical high value for each gate and D FlipFlop logical low value for each gate and D FlipFlop
logical low value for each gate and D FlipFlop

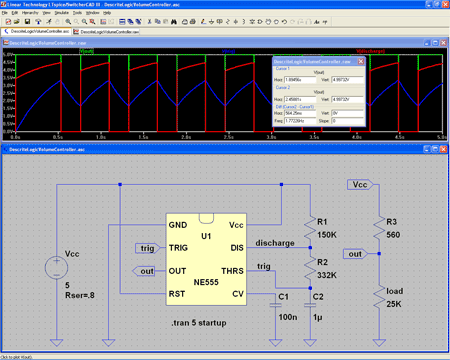
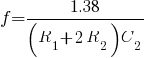
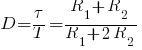
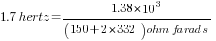
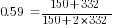
 is frequency in hertz
is frequency in hertz is capacitance in farads
is capacitance in farads is resistance in ohms
is resistance in ohms is duty cycle
is duty cycle is non-zero output duration
is non-zero output duration is the period of the output
is the period of the output
 is defined as a
is defined as a is defined as b
is defined as b
![NPV(CF_k, R, IV) := IV+delim{[}{sum{k=1}{N}{CF_k/(1+R/100)^k}}{]} NPV(CF_k, R, IV) := IV+delim{[}{sum{k=1}{N}{CF_k/(1+R/100)^k}}{]}](https://www.embeddedcomponents.com/wp-content/plugins/wpmathpub/phpmathpublisher/img/math_952.5_bfeb240f8e08138085d65c76df21909d.png)
 is the Net Present Value function, in dollars
is the Net Present Value function, in dollars is a project’s Cash Flow, in dollars
is a project’s Cash Flow, in dollars is the hurdle Rate, in percent per period
is the hurdle Rate, in percent per period is the Initial Investment (a negative number), in dollars
is the Initial Investment (a negative number), in dollars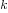 is the cash flow’s time increment, or period
is the cash flow’s time increment, or period is the total number of cash flow periods for
is the total number of cash flow periods for 